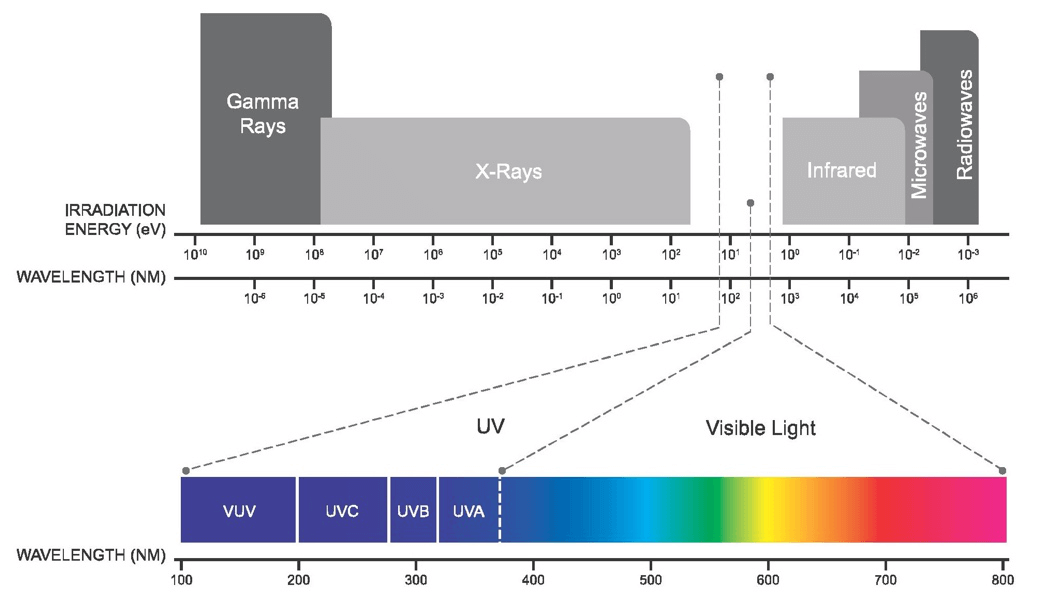
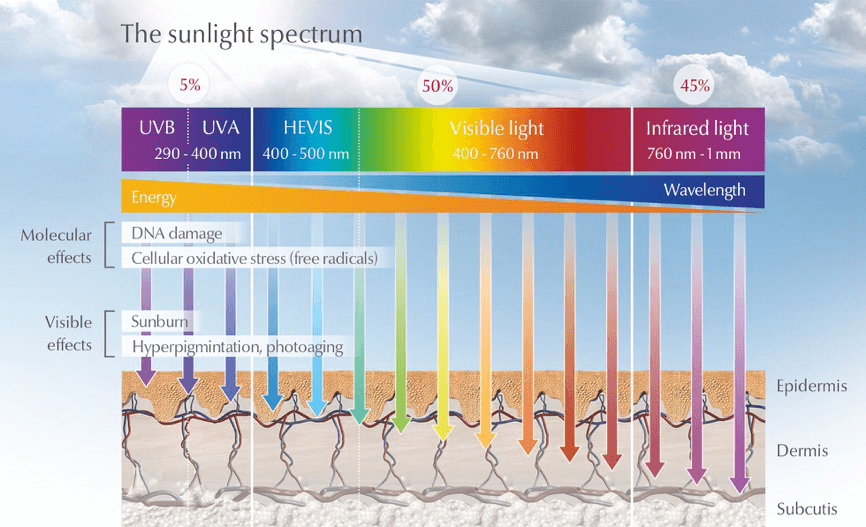
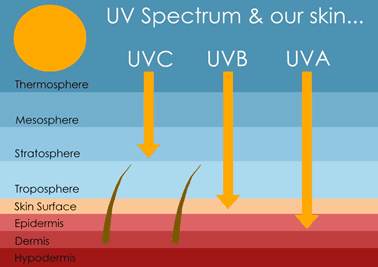
UV light is mainly divided into the following 3 categories according to different biological effects:
- Near ultraviolet (UVA): Longwave Ultraviolet light A with a wavelength of 315~400 nanometers.
- Middle ultraviolet (UVB): Medium wave Ultraviolet light B with a wavelength of 280~315 nanometers will be absorbed by the ozone in the stratosphere.
- Deep ultraviolet (UVC): Short-wave Ultraviolet light C, with a wavelength of 100~280 nanometers, has the weakest UVC penetration ability and cannot penetrate most transparent glass and plastic. The deep ultraviolet light contained in sunlight is almost completely absorbed by the ozone layer and will not reach the earth's surface.